Sunspots and Solar Flares
https://spaceplace.nasa.gov/solar-activity/en/
The Short Answer:
What are sunspots and solar flares?
Sunspots are areas that appear dark on the surface of the Sun. They appear dark because they are cooler than other parts of the Sun’s surface. Solar flares are a sudden explosion of energy caused by tangling, crossing or reorganizing of magnetic field lines near sunspots.

The surface of the Sun is a very busy place. It has electrically charged gases that generate areas of powerful magnetic forces. These areas are called magnetic fields. The Sun’s gases are constantly moving, which tangles, stretches and twists the magnetic fields. This motion creates a lot of activity on the Sun's surface, called solar activity.
Sometimes the Sun’s surface is very active. Other times, things are a bit quieter. The amount of solar activity changes with the stages in the solar cycle. Solar activity can have effects here on Earth, so scientists closely monitor solar activity every day.
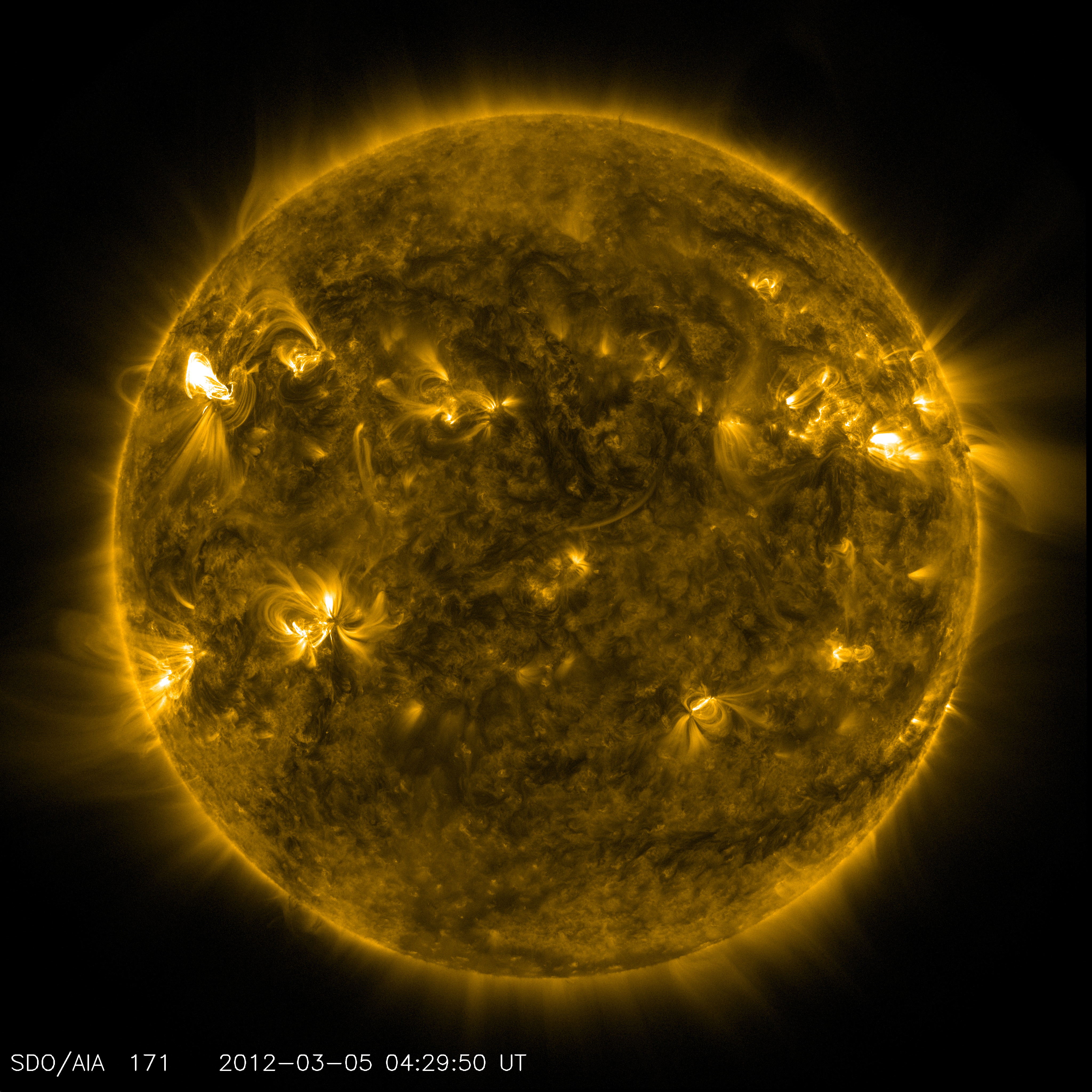
An image of active regions on the Sun from NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory. The glowing hot gas traces out the twists and loops of the Sun’s magnetic field lines. Image credit: NASA/SDO/AIA
Sunspots
Sunspots are areas that appear dark on the surface of the Sun. They appear dark because they are cooler than other parts of the Sun’s surface. The temperature of a sunspot is still very hot though—around 6,500 degrees Fahrenheit!
Why are sunspots relatively cool? It’s because they form at areas where magnetic fields are particularly strong. These magnetic fields are so strong that they keep some of the heat within the Sun from reaching the surface.
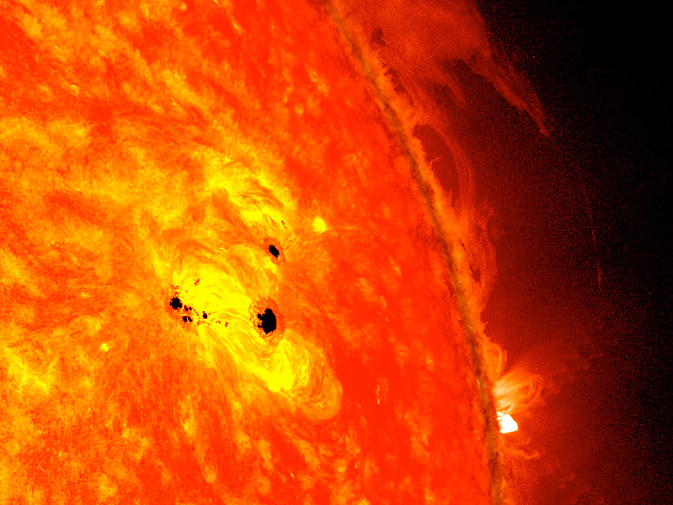
In this image, you can see an active region on the sun with dark sunspots. Image credit: NASA/SDO/AIA/HMI/Goddard Space Flight Center
Solar Flares
The magnetic field lines near sunspots often tangle, cross, and reorganize. This can cause a sudden explosion of energy called a solar flare. Solar flares release a lot of radiation into space. If a solar flare is very intense, the radiation it releases can interfere with our radio communications here on Earth.
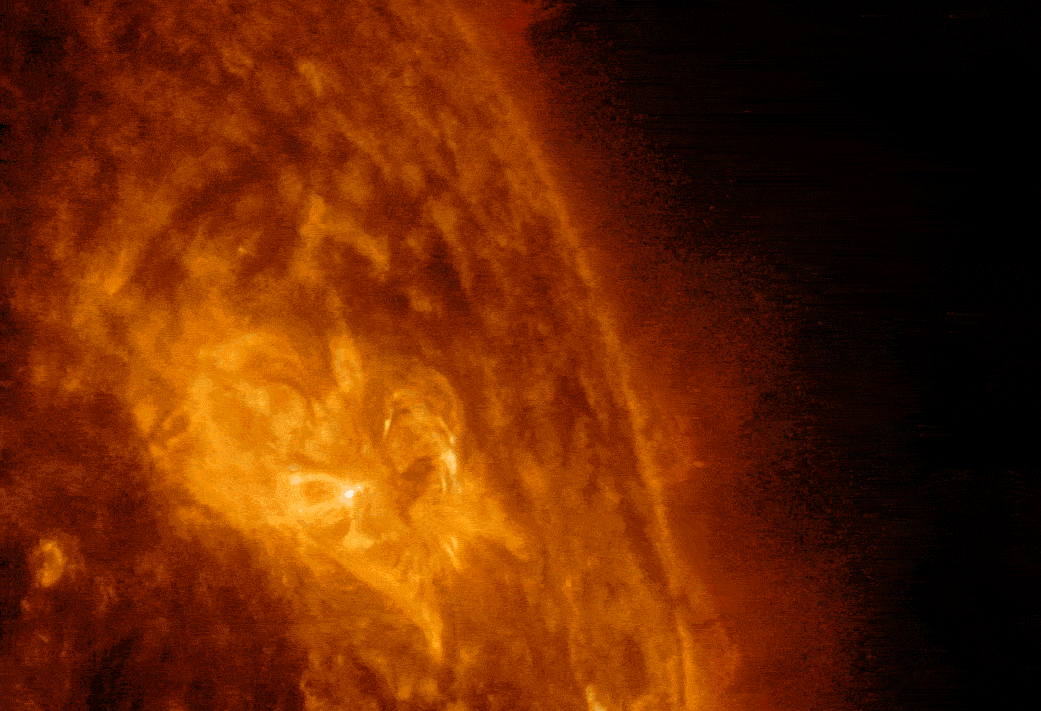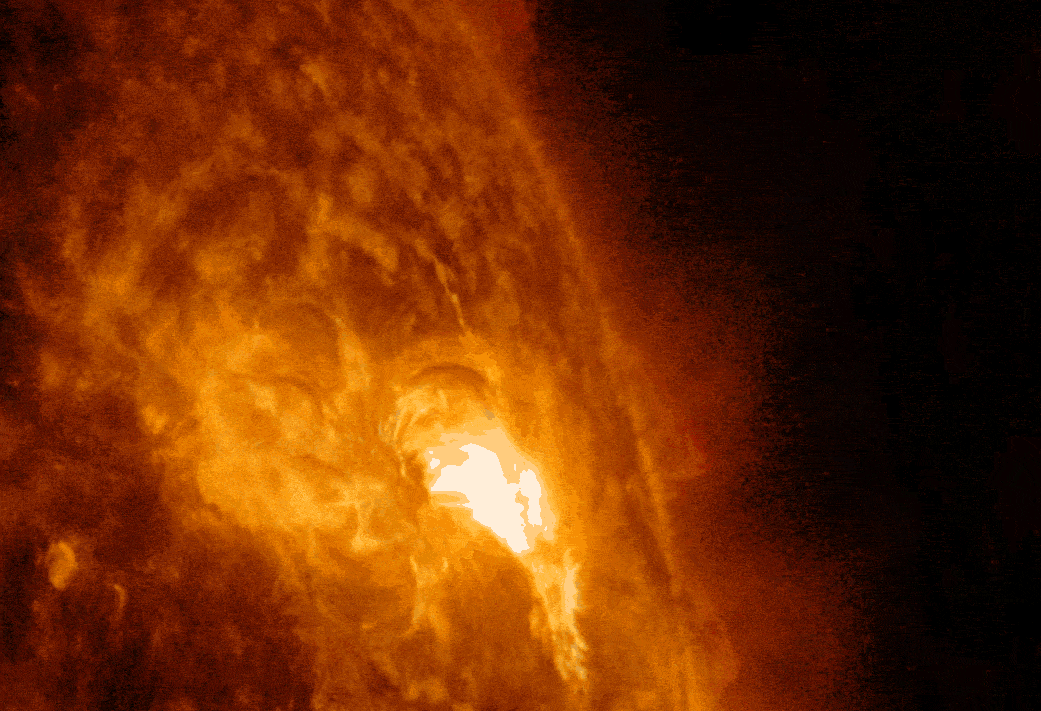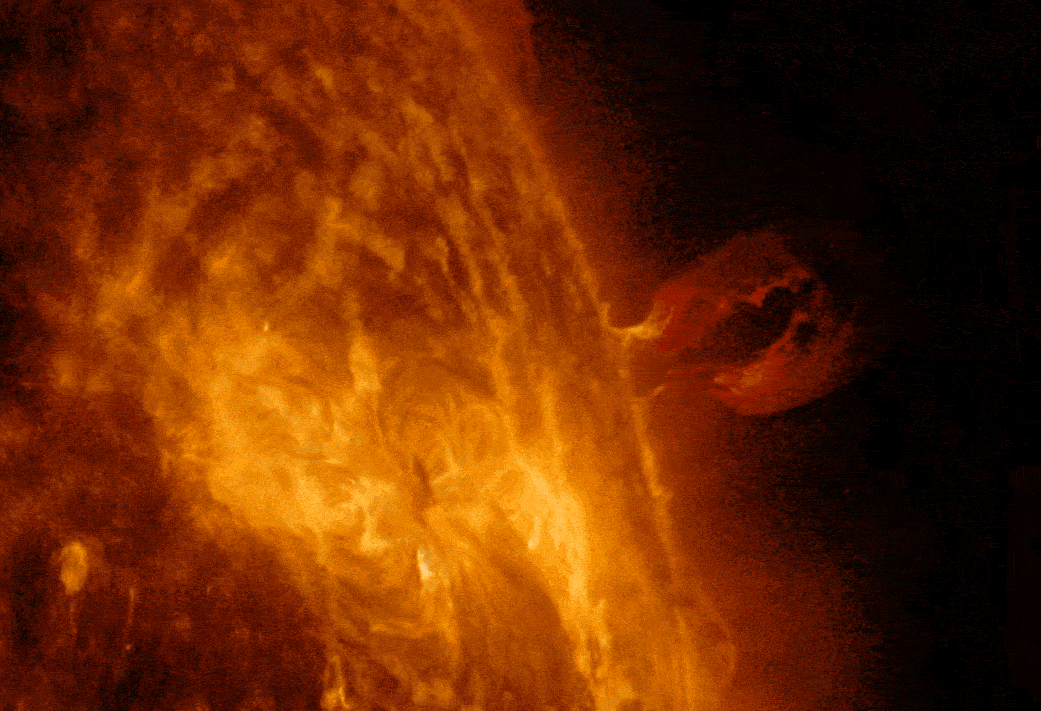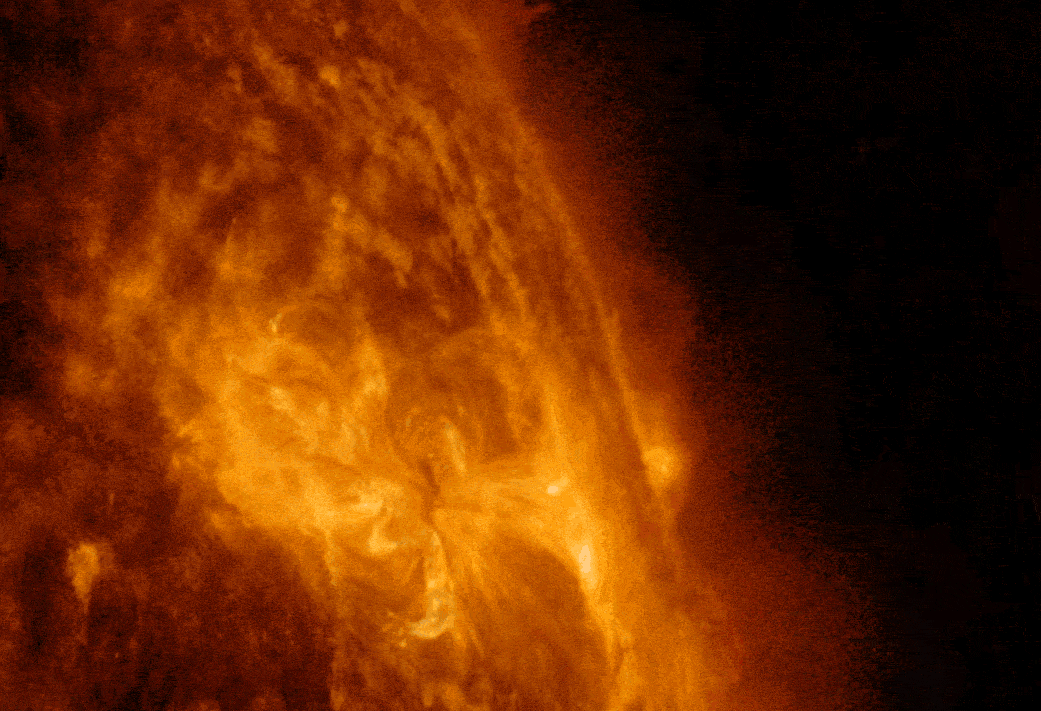
NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory captured this imagery of a solar flare, as seen in the bright flash. A loop of solar material, a coronal mass ejection (CME), can also be seen rising up off the right limb of the Sun. Image credit: NASA/SDO/Goddard
Solar flares are sometimes accompanied by a coronal mass ejection (CME for short). CMEs are huge bubbles of radiation and particles from the Sun. They explode into space at very high speed when the Sun’s magnetic field lines suddenly reorganize.
Effects of Solar Activity on Earth
When charged particles from a CME reach areas near Earth, they can trigger intense lights in the sky, called auroras. When particularly strong, a CME can also interfere in power utility grids, which at their worst can cause electricity shortages and power outages. Solar flares and CMEs are the most powerful explosions in our solar system.
VIDEO: https://youtu.be/GrnGi-q6iWc
CAPTION: On August 31, 2012 a long filament of solar material that had been hovering in the sun's atmosphere, the corona, erupted out into space at 4:36 p.m. EDT. The coronal mass ejection, or CME, traveled away from the sun at over 900 miles per second. This movie shows the ejection from a variety of viewpoints as captured by NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO), NASA's Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory (STEREO), and the joint ESA/NASA Solar Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO).


No comments:
Post a Comment